|
پروفسور محمد حسین سلطان زاده
استاد
دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
متخصص کودکان ونوزادان
طی دوره بالینی عفونی از میوکلینیک آمریکا
دبیر برگزاری کنفرانس های ماهیانه گروه اطفال
دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
|
خانم دکتر فاطمه مهتا
بصیر
عضو هیئت علمی دانشگاه
فوق تخصص نوزادان
به اتفاق اعضای
هیئت علمی
بخش کودکان
بیمارستان شهدای تجریش
معرفی کیس:اقاي دكترسامعي
رزيدنت بيمارستان
شهدا
اقاي دكتر هادي جعفري
تبار
رزيدنت بيمارستان
مفيد
خانم دكتر نوشا محمدي
رزيدنت بيمارستان
امام حسين
|
خانم دکتر
فاطمه مهتا بصیر
عضو هیئت علمی دانشگاه
فوق تخصص نوزادان
به اتفاق اعضای هیئت علمی
بخش کودکان بیمارستان شهدای تجریش

پاسخ:
تشخيص هاي افتراقي:
خانم دکتر
فاطمه مهتا بصیر
عضو هیئت علمی دانشگاه
فوق تخصص نوزادان
به اتفاق اعضای هیئت علمی
بخش کودکان بیمارستان شهدای تجریش
Immune
Thrombocytopenic Purpuras & Pregnancy
Maternal Disease
~ 1-2 cases / 1000
pregnancies
Platelets count < 20.000
: treatment needed. if > 50.000 : NVD or C/S
Mother's treatment by
IVIG, can not treat fetus.
10% to 20% fetus are
affected. Intra-uterine fetal hemorrhage have not been reported.
Management of the newborn
Careful follow-up during the first week: after birth platelets count may
continue to decrease.
US
imaging of brain if platelets < 50.000
platelets < 20.000 : transfusion and/or IVIG
IC
hemorrhage or any other bleeding manifestation : transfusion and IVIG or
glucocorticoid therapy.
Hematuria in Newborn Babies
Causes
Most
frequent : A T N [ perinatal asphyxiation, sepsis, nephrotoxic drugs]
Renal Venous Thrombosis [ gestational diabetes, congenital cyanotic heart
diseases, indwelling venous umbilical catheter]
UTI
and other causes : trauma, neoplasia , abnormalities of coagulation and
thrombocytopenia
Differential diagnosis
Extraurinary sources (
vaginal, prepuce, perineal, rectal)
Myoglobinuria ( inherited
metabolic myopathy , infectious myositis, rhabdomyolysis ) dipstick +
Hemoglobinuria (
erythroblastosis fetalis or other hemolysis)
Pigmenturia ( bile, urate
crystal , porphyrin) dipstick -
معرفي كيس:
معرفی کیس:اقاي دكترسامعي
رزيدنت بيمارستان شهدا

تشخیص های افتراقی:
اقاي دكتر هادي جعفري
تبار
رزيدنت بيمارستان مفيد

خانم دكتر نوشا محمدي
رزيدنت بيمارستان امام حسين

اقاي دكتر هادي جعفري
تبار
رزيدنت بيمارستان مفيد
بسم الله الرحمن الرحیم
چهارشنبه 4/8/90
دکترهادی جعفری تبار
Mother ITP=?
Because an ITP-like syndrome can be seen in patients with
HIV or hepatitis C infection.
Secondary ITP may be induced by Drugs or
occur in patients with Collagen vascular disease .
the diagnosis can be confirmed by appropriate laboratory and
radiologic studies
Thrombocytopenia in
neonate:
DEFINITION :
Historically, neonatal thrombocytopenia has been defined as a
platelet count less than 150,000/microL based upon the definition used in
adults, which corresponds to values at or below the 5th percentile. However,
healthy preterm and term newborns have counts significantly below this level.
CLASSIFICATION :
Platelet size : large, normal, small
Mode: acquired or congenital
Pathologic mechanism involved
Increased consumption of platelets
Immune thrombocytopenia (Autoimmune, Alloimmune,
Drug-induced Peripheral consumption)
Hypersplenism ( Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, Disseminated
intravascular coagulation , Infection, Drug toxicity, Procedure-related,
following exchange transfusion )
Miscellaneous (Neonatal cold injury, Von Willebrand
disease
Decreased production of platelets
Congenital
thrombocytopenias ,Infiltrative disorders Infections: bacterial, viral, or
fungal Drug toxicity
Causes of neonatal thrombocytopenia:
Destructive mechanisms , Immune-mediated
thrombocytopenia: ( The most common cause)
Immune (idiopathic) thrombocytopenic purpura
Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia
Drug-induced thrombocytopenia (heparin, valporate,…)
Autoimmune disorders (APS , SLE)
Sequestration and trapping (hypersplenism)
Mechanical destruction(hemodialysis, cardiopulmuonary
bypass)
Platelet activation and consumption(TTP, HUS)
Impaired PLT
production:
Infection (EBV, CMV, Varicella,
Parvovirus)
Cyanotic heart disease
Bone marrow failure or
infiltration (aplastic anemia ,chemotherapy…)
Nutritional deficiencies (Vit
B12, Folat, Fe)
Genetic cause:
TAR syndrome
Congenital amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
Giant platelet disorder:( Bernard-Soulier syndrome, gray
platelet syndrome)
Miscellaneous :
Phototherapy
Perinatal aspiration syndrome
Persistent pulmonary hypertension
Rhesus alloimmunization
Polycytemia
Metabolic
Post exchange transfusion
Maternal HELLP syndrome
Approach to the thrombocytopenic
newborn infant:
Well Infant:
Maternal History:
History of immune
thrombocytopenic purpura or systemic lupus erythematosus?
Previous infant with
thrombocytopenia or family history of thrombocytopenic neonate?
Infections during pregnancy?
Drug use during pregnancy?
Maternal platelet count
Decreased, suggests autoimmune
Normal, may be autoimmune or alloimmune process
Neonatal examination:
Does
the child look abnormal?
Thrombocytopenia with absent
radii Fanconi anemia
Sick Infant:
Neonatal history:
Is
there a history of perinatal asphyxia?
Does the child have meconium aspiration syndrome or respiratory distress
syndrome?
Is
there evidence of infection?
Necrotizing enterocolitis Sepsis/disseminated intravascular coagulation
Does the child look abnormal?
Toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex Chromosome abnormality
Is
the child small for gestational age?
Could the child have a thrombus?
Were there indwelling catheters?
Did the child have an
intracranial hemorrhage?
Maternal history:
Prenatal or perinatal infection
Preeclampsia, hemolytic anemia,
elevated liver enzymes, low platelet count
Abnormal placenta
Neonatal examination :
Head circumference, weight
percentile
Congenital anomalies: radial
rays, thumbs, dysmorphic features
Hepatosplenomegaly
Blueberry muffin rash
Hemangioma
Neonatal laboratory values:
Abnormalities in the white blood
cell count or hematocrit Hyperbilirubinemia or liver function test
abnormalitites
Evidence of coagulopathy or DIC
Hematuria:
Hematuria is the medical term
for blood in the urine. (presence of more than 5 RBC's in repeated urinary
sediments.)
Gross hematuria : means
that blood can be seen in the urine with the naked eye because it turns the
urine pink, red, or tea-colored. If you see blood in your child's urine, you
should call your child's healthcare provider.
Microscopic hematuria :
means that the urine is normal in color, but it has an increased number of red
blood cells (blood) as seen with a microscope. If your child's urine dipstick
shows blood in the urine, the urine should be examined with a microscope to
confirm that blood is present.
Causes
of Hematuria(gross):
Trauma Causes
Iatrogenic, Self Induced Disorders
Surgical, Procedure Complication
Infectious Disorder (Specific Agent)
Infected organ, Abscesse
Neoplastic Disorders
Allergic, Collagen, Auto-Immune Disorders
Metabolic, Storage Disorders
Biochemical Disorders
Congenital, Developmental Disorders
Hereditary, Familial, Genetic Disorders
Usage, Degenerative, Necrosis, Age Related Disorders
Anatomic, Foreign Body, Structural Disorders
Drugs
Heirarchical Major Groups(Urinary
tract disorders )
Reference to Organ System
Poisoning (Specific Agent)
Causes of heme-negative red urine
Medications :
Doxorubicin, Chloroquine ,Deferoxamine,
Ibuprofen, Iron, sorbitol Nitrofurantoin, Phenazopyridine, Phenolphthalein,
Rifampin,
Food dyes:
Beets (in selected patients)
Blackberries ,Food coloring
Metabolities:
Bile pigments, Homogentisic
acid, Melanin, Methemoglobin ,Porphyrin Tyrosinosis, Urates
Causes
in Neonates:
common
Thrombosis (renal vein or artery)
Nephrolithiasis (including hypercalciuria)
Obstruction(hydronephrosis , PUV)
Reflux
Cystic disease
Syphilis(congenital)
meatal or urethral bleeding
Rare
Mesoblastic nephroma
Wilms tumor
Factious causes
sponge kidney
Coagulation abnormalities and hemoglobinopathies
Algorithm for
gross or symptomatic microscopic hematuria
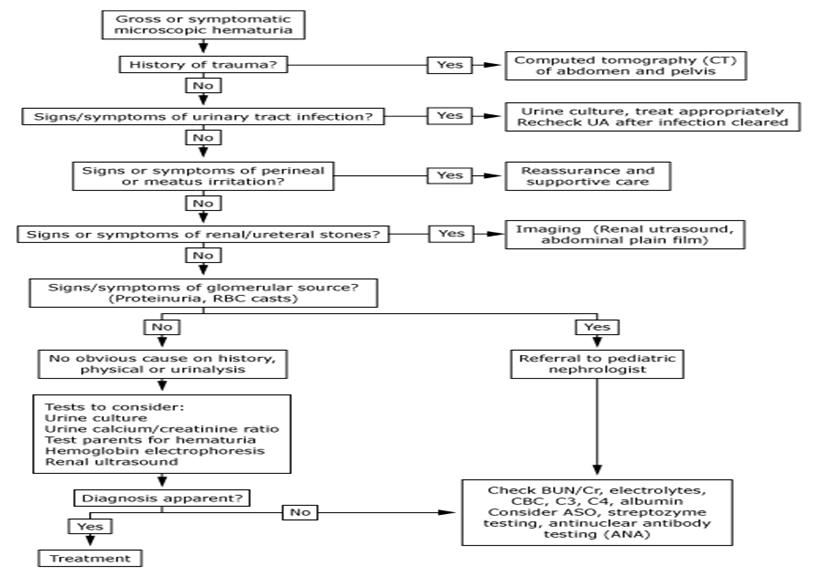
Diagnostic
algorithm for asymptomatic microscopic hematuria with proteinuria
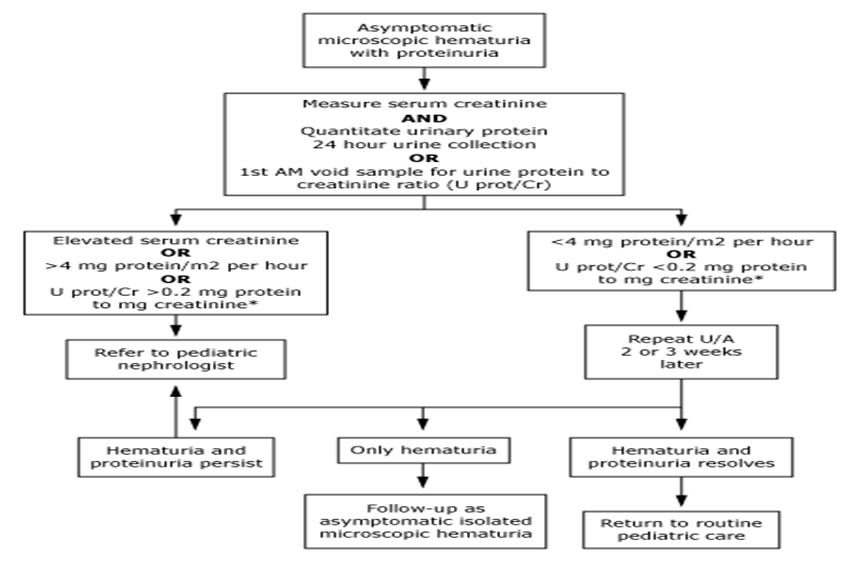
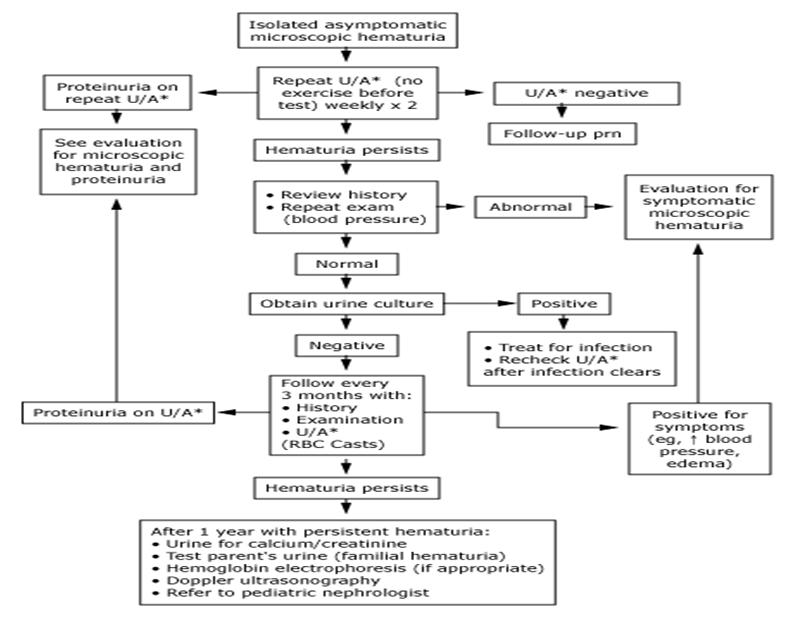
Algorithm for
isolated asymptomatic microscopic hematuria
Thank for
attention
خانم دكتر نوشا محمدي
رزيدنت بيمارستان امام حسين
نوزاد 8 روزه با هماچوری
نوزاد پسر 8 روزه ای با شکایت هماچوری واضح مراجعه میکند.
نوزاد حاصل بارداری ترم
GA=38w
و سزارین میباشد که با آپگار مناسب متولد میگردد.
مادر G2P2Ab0
میباشد و مبتلا به
ITP
از 4 سال قبل که تحت درمان نامنظم با پردنیزولون و فاموتیدین بوده است.
نوزاد شب قبل از مراجعه 3 نوبت هماچوری واضح داشته است. در صبح روز بستری کمی بیحال
بوده ولی علایم شوک و کاهش پرفوزیون محیطی نداشته است.
در معاینه پوست و تنه ایکتریک بوده ولی پتشی و پورپورای قابل ملاحظه نداشته است.
ژنیتالیا طبیعی و ختنه نشده است.
سایر معاینات طبیعی میباشد.
وزن تولد = 2920 وزن هنگام مراجعه = 2950
Lab test, first
day:
U/A : colour= red SG=1008
PH= 7 Pr= 3+
Glu= - Ket= -
Blood=3+ WBC=2-3 RBC= many LE= -
CBC/Diff : Hgb=14.1 Hct=38.9
MCV=93.5
MCH=33.9 PLt=49000
WBC=11.600 N=48% l=50%
M=2%-
Bil=12.3 Dir=0.5
Lab TEST, SAME DAY
:
U/A : colour=yellow app=
clear PH=6.5 SG=1002 Pr=trace WBC=5-6 RBC=1-2
bac= - U/C= -
CBC/Diff : Hgb=12.4 Hct=33.2
Pt=56000
WBC=14000 N=45% l=55%
Ret=1.3% ESR=5 CRP=3mg/dl
BS=65 BUN=8 Cr=0.3 Na=144
K=5.7 Ca=10.5
Bil=12.8 Dir=0.4 PT=14
PTT=29 INR=1.2
G6PD=suff
DAY 2 : U/A : WBC=5-6
RBC=1-2
DAY 3 : U/A : WBC=2-3
RBC=1-3
Day 4 : morning= U/A :
WBC=3-5 RBC=6-8
Blood=+1
Evening= U/A : WBC=2-3
RBC=2-3
Blood=+1
DAY 6 : U/A : WBC=0-1
RBC=0-1
DAY 7 : U/A : WBC=2-3
RBC=3-5 Blood=trace
DAY 10 : U/A : PH=7 SG=1010
Pr= - Glu= -
Bil= - Crystal=- Cast= -
Blood= -
App=clear WBC=0-1 RBC=0-1
Day 1 : Hgb=12.4
Plt=50,000
Day 3 : Hgb=10.9
Plt=97,000
Day 4 : Hgb=11.7
Plt=114,000
Day 5 : Hgb=10.1
Plt=97,000
Day 6 : Hgb=10,5
Plt=141,000
هماچوری ماکروسکوپیک دو نوبت در بیمارستان مشاهده شد که در هر دو نوبت پلاکت بیمار
بیش از 100000 بود.
گرافی توراکوابدومن نرمال بوده است.
سونوگرافی مغز نرمال.
سونوگرافی کلیه در روز سوم بستری: کلیه راست=45mm
کلیه چپ=46mm
و ضخامت پارانشیمال طبیعی.شواهدی به نفع سنگ یا ضایعه فضاگیر نداشت.قطر لگنچه در
کلیه چپ 32mm
AP
میباشد که نشاندهنده
mild stasis
است.
شواهدی به نفع هیدرونفروز در کلیه راست دیده نمیشود.
Diff Diagnosis :
ATN
Cortical
necrosis
Vascular
disease (RVT , RAT )
Bleeding &
Clotting disorder
Urological
Abnormalities
UTI
Glomerular
Disease
Tumors (
Wilms , Neuroblastoma ,Angioma)
Nephrocalcinosis
Trauma











