|
پروفسور محمد حسین سلطان زاده
استاد
دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
متخصص کودکان ونوزادان
طی دوره بالینی عفونی از میوکلینیک آمریکا
دبیر برگزاری کنفرانس های ماهیانه گروه اطفال
دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
|
خانم دكتر سهيلا خليل زاده
عضو هيئت علمي دانشگاه به اتفاق اعضاي هيئت
علمي گروه اطفال بيمارستان مسيح دانشوري
خانم دكتر خديجه رياضي كرماني
معرفي كيس
خانم دكتر فاطمه پژوهنده
رزيدنت بيمارستان لقمان حكيم
خانم دكتر مريم نوري
رزيدنت بيمارستان مفيد
خانم دكتر ناديا دانائي
رزيدنت بيمارستان امام حسين
خانم دكتر انسيه اميري
رزيدنت بيمارستان شهدا
اقاي دكتر حسين علي غفاري پور
فلوشيپ ريه
اقاي دكتر مصلحي
فلوشيپ ريه
اقاي دكتر طباطبائي
فوق تخصص ريه
خانم دكتر محبوبه منصوري
فوق تخصص ايونولوژي و الرژي
خانم دكتر شيرواني
فوق تخصص عفوني اطفال
خانم دكتر خان بابائي
فوق تخصص ريه اطفال
|
خانم دكتر سهيلا خليل زاده
عضو هيئت علمي
دانشگاه به اتفاق اعضاي هيئت علمي گروه اطفال بيمارستان مسيح دانشوري

تشخيص:
Invasive
Aspergillosis
CGD
خانم دكتر خديجه رياضي كرماني
معرفي كيس

تشخيص هاي افتراقي:
خانم دكتر فاطمه پژوهنده
رزيدنت
بيمارستان لقمان حكيم

Problem
list:
A 13 year old boy presented with
Fever
Weight loss
Right hemithorax pain
History of previous exposure to active pulmonary
TB
History of left inguinal tenderness one month
before
PH/E
Tachycardia
Lung auscultation:crackles
Lab data
ESR 120
CRP 74
WBC 13000
HB 9.1
MCV 69
PLT 850
Cr 1.6
INR 1.7
PPD 12
RADIOLOGIC FINDINGS
a right paracardiac soft tissue is noted with some area of air
bronchogram and consolidation pattern at the center of the lesion wich has mass
like appearance
CULTURE
aspergillus
beta hemolytic strep non group
A B C D CC:1000
coagolase negative staph CC:1000
INFECTION
TUBERCULOSIS
ACTINOMYCOSIS
FUNGAL LUNG INFECTION:
Aspergillosts
Blastomycosis
Histoplasmosis
PARASITIC LUNG INFECTION
PCP
LUNG ABSCESS
GRANULOMATOUS INFLAMMATORY DISORDERS
Wegeners granulomatosis
Sarcoidosis pulmonary
Churg-strauss syndrome
ALLERGIC .COLLAGEN.AUTO-IMMUNE
DISORDERS
Eosinophilic pneumonia
Loefflers eosinophilic pneumonitis
NEOPLASTIC
DISORDERS
Hodgkins disease
Metastatic lung disease (ostosarcoma) (RCC)
Leukemic/lymphocytic lung infiltrate
Pulmonary lymphangiomatosis
VASCULAR DISORDERS
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary infarction
POISINING
Silicosis
Pneumoconiosis
IMMUNODEFICIENCY
Bruton agammaglobuulinemia
Common variable immunodeficiency
Human immunodeficiency virus infection
Job syndrome
Severe combined immunodeficiency
Chronic
granulomatous disease
RESULTS
TB
FUNGAL LUNG INFECTION
WEGNERS GRANULOMATOSIS
CGD
METASTATIC LUNG DISEASE
HODGKINS DISEASE
RECOMMENDATION
SPIRAL CHEST CT SCAN WITH CONTRAST
OPEN BX
WATERS X RAY / CT SCAN
NBT
BONE SCAN
ANCA
خانم دكتر مريم نوري
رزيدنت بيمارستان
مفيد

خرد هر کجا گنجی آرد پدید
ز نام خدا سازد آن را کلید
Problem List
Fever+ weight loss
Left groin pain
Right hemithorax pain
No response to antibiotic
therapy
Active TB exposure
Lab test
plt=850000
ESR=120 corrected ESR=96
CRP=74
PT=16.7 INR=1.7
PPD=12
Imaging
CXR: Right paracardiac consolidation
Bronchoscopy culture:
Aspergillus
Pathology
Pulmonary eosinophilic infiltration
Missing Points
Groin pain?
Respiratory Symptoms?
Extra pulmonary signs and
symptoms?
History of prior infections?
Response to immunization?
Exact time of TB exposure?
Drug History?
Travel History?
Eosinophil count?
Igs level?
Prick test?
Immune system work-up?
Collagen vascular diseases’
work-up?
Sweat test?
S/E * 3
Sputum Smear and PCR NOT
gastric washing
BAL: total and diff of
leukocyte count?
Causes of
Pulmonary Eosinophilia
Drug and toxin-induced
eosinophilic lung diseases
NSAIDs, Antimicrobials,
Phenytoin
Helminthic and fungal infection-related
Transpulmonary passage of larvae (Loffler’s
Syndrome)
Pulmonary parenchymal invasion
Heavy hematogenous seeding(
Strongyloidiasis,Trichinosis)
Tropical pulmonary
eosinophilia
ABPA
Acute eosinophilic pneumonia
Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia
Churg Strauss Syndrome
Other (Idiopathic, Neoplasm)
Differential
Diagnosis
TB
Active TB exposure +
Radiologic changes+ PPD
Sputum Smear and PCR? Tissue
PCR?
ABPA
Hypersensitivity reaction when
bronchi becomes colonized with Aspergillus.
Aspergillus is cultured from
the sputum in up to two-third of patients with ABPA.
Range of clinical manifestation(asymptomatic
pulmonary consolidation
–
fever and respiratory symptoms and signs)
The major diagnostic
features: A history of asthma
Immediate skin test reactivity
to Asp. Antigen
Percipitating serum Ab to
A.fumigatus
Serum Total IgE>417 IU/ml
Periph.Blood Eos>500
Imaging
Elevated specific serum IgE
and IgG to A.fumigatus
Prick test, IgE
level?
Differential
Diagnosis
Helminthic parasitic
infections
Loffler’s
Syndrome Respiratory symptoms and signs
Transient pulmonary
infiltrates
Eosinophilia
S/E * 3? Serologic tests?
Sputum analysis(Strongyloides)? Blood Eos count?
Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Abnormal accumulation of eos.
In the lung
Subacute illness
Fever+cough+weight
loss+wheezing+night sweats
Peripheral eosinophilia is
common
CXR
Differential
Diagnosis
CVID
Decreased IgG with Low level
of IgA+/- IgM
Poor or absent response to
immunization
Age of onset after puberty
Broad spectrum of disorders (infections,
chronic lung disease, GI and liver disorders,…)
Normal physical examination
Increased risk of malignancies
Serum concentration of IgG?
Response to immunization? GI symptoms?
S/E * 3?
Differential
Diagnosis
Churg Strauss Syndrome
Sinusitis+ Asthma+ Prominent
peripheral blood eosinophilia
Lung Biopsy
History of prior infections?
Drugs and Toxins
Range of clinical presentation
Asymptomatic pulmonary
infiltration with eosinophilia to chronic cough with or without dyspnea and
fever to acute eosinophilic pneumonia
History of groin pain and
possible NSAIDs consumption
Elevated PT
Drug History?
خانم دكتر ناديا دانائي
رزيدنت بيمارستان
امام حسين

Problem list
13 Y , BOY
Lt inguinal pain & Rt hemithorax pain from 1M
ago
Fever & weight loss
Non response to IV antibiotic therapy
Hx of contact to TB
Diffuse crackle
Lab data:
WBC:13000 diff:PMN:76% ,L:15%
HB:9.1
PLT:850000
ESR:120 CRP:74
Cr:1.6
S/E:fatty droplet positive
pT:16.7 INR:1.7
PPD:12
CXR=Rt paracardiac consolidation
CHEST HRCT=a RT paracardiac soft tissue is
noted with some area of air bronchogram & consolidation pattern at the center
of the lession which has mass like appearance, at the periphery of the mass
some lymphangiectasia
Direct smear=NL
Culture=aspergillus
TBLB=pulmonary eosinophillic infiltration
BMB=chronic inflammatory with mild
eosinophillic infiltration
DDX
1.TB
*AFB (BAL,TBLB)
2.eosinophilic lung dis.
. ABPA
. eosinophilic pneumonia
. loffler syndrom
. churg-strauss syndrom
*serum percipitant test
*Aspergillus skin test
*serum Ig E
*CBC ,diff(EO)
*P-ANCA
3.CVD
C-ANCA,P-ANCA,ANA,
*C3,C4,CH50
*HIV Ab,HBS Ag,HBS Ab,HCV Ab
4.Malignancy (lymphoma)
*mediastinal HRCT
5.Non classified
Aspergillosis in immunocompromised patient:
. N or MQ dysfunction : CGD , SCID
.HIV
*NBT TEST
*Ig
*CD4
primary malignancy of bone
*immaging
*Ca,ph,Alkp
CF
With thanks
خانم دكتر انسيه اميري
رزيدنت بيمارستان
شهدا

Case presentation
E. Amiri MD
Problem list
Fever
Hemithorax pain
Weight loss
Inguinal pain
Right paracardiac consolidation
History of contact with active TB patient
FTT
Generalized crackle in both lungs
Lab tests
CRP : 74
ESR : 120 (corrected:72)
WBC : 13,000 (P : 76%- L : 15% )
Hb : 9.1
MCV : 69
PT : 16.7
PTT : 48
S/E : fatty droplets
PPD : 12 mm
Imaging study
Lung CT scan : Consolidation – airbronchogram
Bronchoscopy : Nl
Culture : Aspergillus sp
Pathology
Pulmonary eosinophilic infiltration
Differential Diagnosis
Eosinophilic pneumonia
Aspergilloma- invasive form :
Vasculsar involvement
High eosinophilia
ABPA :
Secondary to CF , TB cavity , Asthma
↑ Eos
↑ IgE
Bronchiectasis
Recurrent pneumonia
Parasites :
↑ Eos
Granuloma
Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia :
Secondary to asthma and allergy
Bilateral lung involvement
Churg-strauss syndrome & Sarcoidosis :
↑ Eos
Granuloma
Old age
TB
History of contact
PPD=12 mm
Pulmonary symptoms
Malignancy (associated with pulmonary
involvement) :
Histyositosis :
Bone tumors
Eosinophilia
Respiratory distress
hepatosplenomegaly
Seborrheic dermatitis
Otorrhea
Bone marrow involvement
Ewing sarcoma
Fever
Systemic symptoms
Bone involvement in Ph/E and CT scan
Lymphoma
Mediastinal involvement
Lymphadenopathy
Pulmonary involvement
Bone marrow involvement
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Soft tissue involvement
Pulmonary involvement
Neuroblastoma
Posterior medistinal involvement
Pulmonary involvement
CF
FTT
Pulmonary involvement
Fatty droplets in S/E
اقاي دكتر حسين علي غفاري پور
فلوشيپ ريه

13 year/old boy,from Tabriz live in tehran
CC:fever&pain of left inguinal
PI:1month before admission:
Pain of left inguinal,no trauma
low grade fever
Sometimes coughing & right hemithorax chest
pain
malaise&weight loss
PMH:
Term/NVD/ G4P3AB1
No NICU admission
Vaccination:full/development:nl
Hospitalization:90/11/03
FH:TB(+)
DH:(-)
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
GA:alert and ill
no toxic
VS: AT:37 RR:24
PR:120 BP:100/60
weight(for age percentiles):5%
height(for age percentiles):25%
H&N:conjunctive:pale & no lymphadenopathy
Heart:nl
Lung:fine crackles
Abdomen:no organomegaly
Extremities:nl
LAB TESTS
WBC:13000 /N:76%/L:15%
RBC:3500000
HGB:9,1/HCT:28,5/MCV:69/MCH:23,5
/MCHC:33 RDW:16,8
PLT:850000
ESR:120
CRP:74
LDH:261
URIC ACID:2 /ure: 12 /Cr:1,6
ADA:37
PPD:12mm
Gastric washing:
Direct smear:(-)
PCR(for MBT): (-)
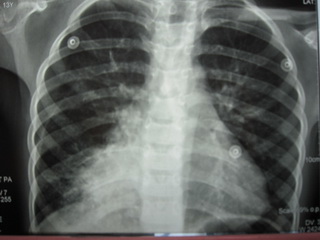
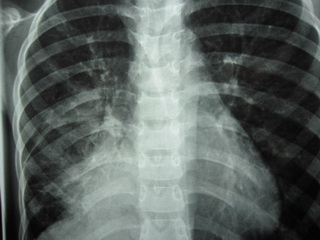
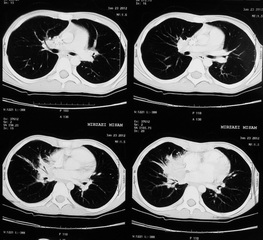
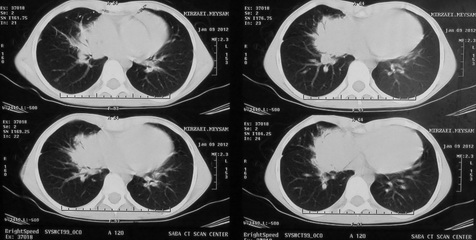
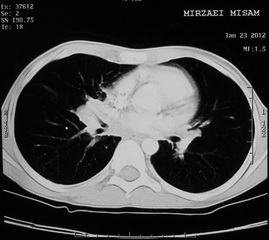
Report of spiral ct scan
A right paracardiac soft tissue is noted,
with some area of air bronchogram and consolidation pattern at the center of the
lesion which has mass like appearance at the periphery of the mass some
lymphagiectasia also seen and right hilum prominency.
Spiral abdomen&pelvic ct scan:
Normal
Bone marrow aspiration:
Normocellular
Bronchoscopy:
Normal
discharge for:
direct- smear:negative
culture:
Aspergillus sp
Pathology
Transbronchial lung biopsy:
pulmonary eosinophilic associated with
chronic non specific inflammatory process.
Negative for malignancy.
Negative for granuloma.
اقاي دكتر مصلحي
فلوشيپ ريه

Question remind unclear
about case
Trend of growth?
Recurrent infectious (pneumonia or AOM or
sinusitis,…)?
Symptoms after vaccination?
Hx of diseases in other sibling
Leg pain?
Hx of trauma?
Night sweating, exertional dyspnea, cough
Cyanosis, Clubbing?
Parental relative?
Drug Hx?
Diff- U/A-BS-LFT
EOSINOPHILIC LUNG DISEASES
(PIE)
Early description :
pulmonary symptoms or CXR abnormalities
and
PB eosinophilia
After 1970 description :
characterized by increase in BAL
eosinophil number but not necessarily blood eosinophils
Some affect the airways
predominantly, some affect the lung parenchyma, and some affect
predominantly the lung vasculature.
From subtle symptoms and are self-limited to
respiratory failure.
Subtype:
Group I, Löffler
syndrome or simple pulmonary eosinophilia
Group II, prolonged pulmonary eosinophilia
Group III, Weingarten’s
syndrome or tropical eosinophilia
Group IV, pulmonary eosinophilia with
asthma
Group V, polyarteritis nodosa
Parasitic infection (Ascaris) & drug
reactions are currently an important etiology
No cause in 1/3 of cases
Mild febrile illness with myalgias
,nonproductive cough, and dyspnea.
No abnormalities on physical examination, but
sometimes a few crackles or wheezes are heard
Parasites That Cause
Eosinophilic Lung Disease
Ancylostoma sp.
Ascaris sp.
Echinococcus sp.
Schistosoma sp.
Strongyloides stercoralis
Toxocara sp.
Trichinella spiralis
Wuchereria bancrofti
Patients with Ascaris infection are usually
febrile with a nonproductive cough and chest pain. In severe cases
hemoptysis occurs.
CXR: abnormalities are usually bilateral and
peripheral, pleural based
Parasites and ova are sometimes found
in the stool after the resolution of the pul. illness
larvae can be isolated from gastric aspirates
or sputum
Weingarten = tropical eosinophilia =
severe spasmodic cough, massive peripheral
eosinophilia, diffuse mottling in both lungs
endemic in India, Sri Lanka due to
Wuchereria bancrofti
DRUG-INDUCED
Cough, dyspnea, and fever
Histologically : interstitial edema with a
lymphocytic and eosinophilic infiltrate, (alveoli contain eosinophils and
histiocytes)
CXR show interstitial or alveolar
infiltrates and Kerley B lines
Skin testing with either patch or prick
tests is usually negative


ACUTE EOSINOPHILIC PNEUMONIA
Idiopathic
febrile illness of 1 to 5 days +
myalgias, pleuritic chest pain, and severe hypoxemia
basilar or diffuse crackles
CXR: diffuse alveolar infiltrates involving
all lobes
Small to moderate-sized pleural effusions are
common
CHRONIC EOSINOPHILIC PNEUMONIA
middle-aged women
fever, night sweats, weight loss
cough, dyspnea, and wheezing (asthma)
lymphadenopathy and hepatomegaly
Pb & BAL eosinophil
ESR & IgE is elevated
CXR; bilateral, peripheral infiltrates
negative image of pulmonary edema =dignostic
CT : peripheral airspace disease and may
show hilar lymphadenopathy
ALLERGIC ANGIITIS AND
GRANULOMATOSIS
allergic rhinitis and asthma for years
peripheral eosinophilia with values up to 80%
small and medium-sized arteries and veins.
sinusitis, rhinitis, and nasal polyps
GI:abdominal pain, diarrhea, bleeding, and
obstruction;
cardiovascular: pericarditis, and heart
failure.
Renal
CNS
CXR: patchy and transient infiltration
Eosinophilic pleural effusions and hilar
adenopathy
IDIOPATHIC HYPEREOSINOPHILIC SYNDROME
elevated eosinophila for >6 months,
or for <6 months with evidence of organ
(heart) damage
most common in adults 20 to 50 years - male
ABPA
1% to 2% of asthmatics and 7% to 9% of cystic
fibrosis
Minimal Diagnostic Criteria:
Acute or subacute clinical deterioration
Total serum IgE >500 IU/mL
Immediate cutaneous reactivity or RAST
(a)IgG antibody to A. fumigatus; or (b) new
or recent abnormalities on CXR or chest CT that have not cleared with
antibiotics and standard physiotherapy
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
HP = extrinsic allergic alveolitis
recurrent inhalation of organic antigens
pet birds
–
molds (Aspergillus, Penicillium)
mean age=10 y
Male
flu-like
syndrome with fever, chills, cough, myalgias, and malaise
leukocytosis with neutrophilia, elevated
CRP & ESR
ill appearing child with dyspnea and
basilar crackles
CXR : bilateral lower lobes reticulonodular
infiltrates
CT: ground-glass appearance and centrilobular
nodules
Acute eosinophilic pneumonia, P. carinii
pneumonia, and some drug induced lung diseases have Eosinophils in the BAL fluid
Acute & chronic eosinophilic pneumonia,
ILD, and tropical eosinophilia usually lead to a restrictive defect
Immunologic:
+ve: Weigh + Aspergillosis
CGD
Hyper IGE (skin-face-teeth-AOM-pneumonia-staph
pneumatoceles-mucocutaneous candidiasis)
Rheumatology:
+ve: Weigh + kidney
PAN (heart-joints-skin-GI-Renal-eye lung-CNS-PNS)
JRA
SLE
DDx lung consolidation + lymphangectasis may
include :
Obstractions
Infections
Aspergillosis (invasive/infection or
allergic)
Ascariasis
Hydatid cyst
TB
Blastomycosis
Cryptococcosis
IDDM
CGD
ABPA (CF)
Lymphoma
TB
PAN-JRA
HIV
TEST
BS
NBT or DHR
àCGD
SCT
IgE - Prick test
–
PFT
Lung Biopsy
اقاي دكتر طباطبائي
فوق تخصص ريه
خانم دكتر محبوبه منصوري
فوق تخصص ايونولوژي
و الرژي
خانم دكتر شيرواني
فوق تخصص عفوني
اطفال
خانم دكتر خان بابائي
فوق تخصص ريه اطفال























