|
پروفسور محمد حسین سلطان زاده
استاد
دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
متخصص کودکان ونوزادان
طی دوره بالینی عفونی از میوکلینیک آمریکا
دبیر برگزاری کنفرانس های ماهیانه گروه اطفال
دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
|
اقاي دکترسيد
احمد طباطبائي
فوق تخصص ريه عضو هيئت علمي
به اتفاق اعضای
هیئت علمی بيمارستان
كودكان مفيد
خانم دكتر الهه موحدي
رزيدنت بيمارستان
مفيد
خانم دكتر مينا دادخواه
رزيدنت بيمارستان
لقمان
خانم دكتر مريم مخملباف
رزيدنت بيمارستان
شهدا
خانم دكتر سولماز حسني
رزيدنت بيمارستان
امام حسين
اقاي دكتر صدر
فلوشيپ ريه
اقاي دكتر مصلحي
فلوشيپ ريه
اقاي دكترغفاري پور
فلوشيپ ريه
اقاي دكتر جفرودي
عضو هيئت علمي
بيمارستان شهدا
خانم دكتر منصوري
فوق تخصص ايمونولوژي
عضو هيئت علمي
بيمارستان مفيد
|
اقاي دکترسيد
احمد طباطبائي
فوق تخصص ريه عضو هيئت علمي
به اتفاق اعضای
هیئت علمی بيمارستان
كودكان مفيد


تشخيص:
Post Operative
TEF
تشخيص هاي افتراقي:
خانم دكتر الهه موحدي
رزيدنت بيمارستان مفيد


Question remind unclear
about case
Trend of growth?
Recurrent infectious (pneumonia or AOM or sinusitis,…)?
Symptoms after vaccination?
Hx of diseases in other sibling
Leg pain?
Hx of trauma?
Night sweating, exertional dyspnea, cough
Cyanosis, Clubbing?
Parental relative?
Drug Hx?
Diff- U/A-BS-LFT
EOSINOPHILIC LUNG DISEASES
(PIE)
Early description :
pulmonary symptoms or CXR abnormalities and
PB eosinophilia
After 1970 description :
characterized by increase in BAL eosinophil number but not necessarily blood
eosinophils
Some affect the airways predominantly, some affect the lung
parenchyma, and some affect predominantly the lung vasculature.
From subtle symptoms and are self-limited to respiratory failure.
Subtype:
Group I, Löffler
syndrome or simple pulmonary eosinophilia
Group II, prolonged pulmonary eosinophilia
Group III, Weingarten’s
syndrome or tropical eosinophilia
Group IV, pulmonary eosinophilia with asthma
Group V, polyarteritis nodosa
Parasitic infection (Ascaris) & drug reactions are currently an
important etiology
No cause in 1/3 of cases
Mild febrile illness with myalgias ,nonproductive cough, and dyspnea.
No abnormalities on physical examination, but sometimes a few crackles or
wheezes are heard
Parasites That Cause
Eosinophilic Lung Disease
Ancylostoma sp.
Ascaris sp.
Echinococcus sp.
Schistosoma sp.
Strongyloides stercoralis
Toxocara sp.
Trichinella spiralis
Wuchereria bancrofti
Patients with Ascaris infection are usually febrile with a nonproductive cough
and chest pain. In severe cases hemoptysis occurs.
CXR: abnormalities are usually bilateral and peripheral, pleural based
Parasites and ova are sometimes found in the stool after the resolution of
the pul. illness
larvae can be isolated from gastric aspirates or sputum
Weingarten = tropical eosinophilia =
severe spasmodic cough, massive peripheral eosinophilia, diffuse mottling
in both lungs
endemic in India, Sri Lanka due to Wuchereria bancrofti
DRUG-INDUCED
Cough, dyspnea, and fever
Histologically : interstitial edema with a lymphocytic and eosinophilic
infiltrate, (alveoli contain eosinophils and histiocytes)
CXR show interstitial or alveolar infiltrates and Kerley B lines
Skin testing with either patch or prick tests is usually negative

ACUTE EOSINOPHILIC PNEUMONIA
Idiopathic
febrile illness of 1 to 5 days + myalgias, pleuritic chest pain, and
severe hypoxemia
basilar or diffuse crackles
CXR: diffuse alveolar infiltrates involving all lobes
Small to moderate-sized pleural effusions are common
CHRONIC EOSINOPHILIC PNEUMONIA
middle-aged women
fever, night sweats, weight loss
cough, dyspnea, and wheezing (asthma)
lymphadenopathy and hepatomegaly
Pb & BAL eosinophil
ESR & IgE is elevated
CXR; bilateral, peripheral infiltrates negative image of pulmonary edema =dignostic
CT : peripheral airspace disease and may show hilar lymphadenopathy
ALLERGIC ANGIITIS AND
GRANULOMATOSIS
allergic rhinitis and asthma for years
peripheral eosinophilia with values up to 80%
small and medium-sized arteries and veins.
sinusitis, rhinitis, and nasal polyps
GI:abdominal pain, diarrhea, bleeding, and obstruction;
cardiovascular: pericarditis, and heart failure.
Renal
CNS
CXR: patchy and transient infiltration
Eosinophilic pleural effusions and hilar adenopathy
IDIOPATHIC HYPEREOSINOPHILIC SYNDROME
elevated eosinophila for >6 months,
or for <6 months with evidence of organ (heart) damage
most common in adults 20 to 50 years - male
ABPA
1% to 2% of asthmatics and 7% to 9% of cystic fibrosis
Minimal Diagnostic Criteria:
Acute or subacute clinical deterioration
Total serum IgE >500 IU/mL
Immediate cutaneous reactivity or RAST
(a)IgG antibody to A. fumigatus; or (b) new or recent abnormalities on CXR or
chest CT that have not cleared with antibiotics and standard physiotherapy
Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
HP = extrinsic allergic alveolitis
recurrent inhalation of organic antigens
pet birds – molds (Aspergillus,
Penicillium)
mean age=10 y
Male
flu-like syndrome
with fever, chills, cough, myalgias, and malaise
leukocytosis with neutrophilia, elevated CRP & ESR
ill appearing child with dyspnea and basilar crackles
CXR : bilateral lower lobes reticulonodular infiltrates
CT: ground-glass appearance and centrilobular nodules
Acute eosinophilic pneumonia, P. carinii pneumonia, and
some drug induced lung diseases have Eosinophils in the BAL fluid
Acute & chronic eosinophilic pneumonia, ILD, and tropical eosinophilia
usually lead to a restrictive defect
Immunologic:
+ve: Weigh + Aspergillosis
CGD
Hyper IGE (skin-face-teeth-AOM-pneumonia-staph pneumatoceles-mucocutaneous
candidiasis)
Rheumatology:
+ve: Weigh + kidney
PAN (heart-joints-skin-GI-Renal-eye lung-CNS-PNS)
JRA
SLE
DDx lung consolidation + lymphangectasis may include :
Obstractions
Infections
Aspergillosis (invasive/infection or allergic)
Ascariasis
Hydatid cyst
TB
Blastomycosis
Cryptococcosis
IDDM
CGD
ABPA (CF)
Lymphoma
TB
PAN-JRA
HIV
TEST
BS
NBT or DHR àCGD
SCT
IgE - Prick test –
PFT
Lung Biopsy
خانم دكتر مينا دادخواه
رزيدنت بيمارستان لقمان
به نام خداوند بخشنده و مهربان
P.I
Female /6
y.o
Wheezing/cough (righte now)/Fever
Cough and
wheezing from neonate period
Congenital esophageal atresia
primary
repair of a congenital EA w/o TEF on the first day of her life.
recurrent pneumonia and wheezy episodes
barium
swallow:NL
unresponsiveness to anti-asthmatic and anti-biotics and anti-reflux treatment
Weight
loss
No
allergy
CXR:
straggly &bilateral , brief grand glass appearance
CT-SCAN:
segmental collapse and alveolar infiltation in lower parts
Bilateral
diffuse nodular opacities and tree in bud pattern accompanied by mosaic
attenuation due to air trapping.
Cylindrical bronchiectasis of lower lobes
Dilatation of esophagus and hiatal hernia
VIRTUAL
BRONCHOSCOPY:NL
PPD:NEG/BK:NEG
Sweat
test:Nl
Immunologic test: Nl
Lab data:
Wbc:24300/neut:90%,lymph:10%
Mcv:50.9/RBC:5,600,000
Plt:605000
Bun:7/cr:0.7
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis, a disease characterized by
irreversible abnormal dilatation and anatomic distortion of the bronchial tree,
likely
represents a common end stage of a number of nonspecific and unrelated
antecedent events.
patients
presented with cough, tachypnea, wheezing, sputum production and failure to
thrive. Clubbing was found in (33%) of the patients. Cyanosis and oxygen
requirement were reported in (23%) of the patients. Hemoptysis was reported.
Bronchiectasis DDx
Pulmonary
Asthma
Kartagener
Foreign
body aspiration
ABPA
Tuberculosis
Bronchogenic cyst
Prematurity
Cystic
fibrosis
TEF
repair
second
congenital fistula
Reccurent
fistula
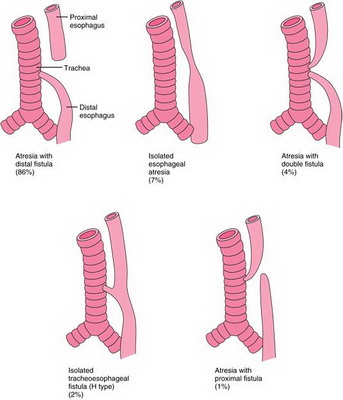
Most
infants with EA with TEF have proximal atresia with distal TEF. They are easily
diagnosed in the first days of life with apparent symptoms and findings and
undergo surgical repair. Since two fistulas with EA occur very infrequently,
proximal fistula may be overlooked during primary surgical repair. An
undiagnosed proximal fistula shares the same clinical features with an isolated
H-type fistula, which is usually diagnosed later, even in adulthood.
Although
symptoms of an undiagnosed proximal fistula may include choking, coughing and
recurrent respiratory tract infections, there may be long and asymptomatic
intervals, which may be explained by the nature of the fistula. The contractions
of the muscle wall of the fistula or the oblique direction of the fistula tract
from the trachea to esophagus may protect the airway from aspiration of foods
during swallowing.
Recurrent
respiratory tract infections and wheezing are commonly reported in infants after
primary repair, but become less frequent over time. Bronchiectasis is a very
unusual complication.
Asthma is
reported in nearly one-fourth of children with repaired EA and TEF. In our
patient, late onset of recurrent bouts of pneumonia and wheezing resulting in
bronchiectasis, unresponsiveness to anti-asthmatic treatment, incompatible with
the diagnosis of asthma raised the possibility of a recurrent TEF or a second
congenital fistula.
In the
pre-operative period, although standard barium swallow failed to show the
fistula, in the prone position confirmed the diagnosis. The presence of a TEF
can also be demonstrated by three-dimensional CT scanning and virtual
bronchoscopy. A dynamic radionuclide gastroesophageal scintigraphy with
technetium- 99m showed a fistulous opening between the trachea and the esophagus
.
Cardiac diseases:
Dextrocardia
Congestive heart failure
Ventricular septal defect
Atrial
septal defect
Pulmonary
hypertension
Mitrale
valve prolapse
Skeletal:
Pectus
excavatum
Scoliosis
Absent ribs
Marfan's syndrome
Immunodefficiency:
Hypogammaglobulinemia
SCIDS
Human
immunodeficiency virus
Hyper
IgE1
IgG
subclass defficiency
Hyper IgM
Whiscott
Aldrich syndrome
Common
variable-Hypogammaglobulinemia
T-cell
deficiency
Barre
lymphocyte syndrome
Central nervous system
disease:
Cerebral
palsy/ seizure disorder
Apnea
Craniosynostosis
Cutis
laxa/ developmental delay
Down syndrome/seizure
Fatty acid oxidation defect
Other
disease associations:
Neuroblastoma
Antithrombin III defficiency
Corrosive
ingestion
Liver cirrhosis
Ethmoid mucocele
Discussion
All
patients with confirmed bronchiectasis had the following tests done:
Respiratory cultures from sputum or from nasopharyngeal aspirates if unable to
produce sputum for culture and sensitivity; PPD skin test; sputum for acid fast
bacilli (AFB) stain and AFB culture, or gastric aspirates instead of sputum
for children who are unable to produce sputum.
(PPD:NEG/BK:NEG)
barium
swallow to rule out
vascular ring or tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF):
barium
swallow:NL
A
dynamic radionuclide gastroesophageal scintigraphy with technetium- 99m
canshowed a fistulous opening between the trachea and the esophagus.
sinus
CT for those who presented
with persistent rhinorrhea for
more than
3 months.
For
patients who had family history of bronchiectasis, nasal brush by specialist
(ENT) or biopsy of airway endothelium for electron microscopy to rule out
immotile cilia syndrome was done.
Pulmonary function test was
done for patients >5 years of age and able to comprehend to test maneuvers.
Associated diseases were investigated according to presenting symptoms or type
of referrals. (For example, magnetic resonance or CT brain was done in
patients with cerebral palsy or central nervous system abnormalities.
Sweat
test: This test is done to
see if your child has cystic fibrosis
Chest
x-ray: A chest x-ray be
used to check heart, lungs, and chest wall.
Echocardiography:
Heart
disease
Result
1)second
congenital fistula
2)Cystic
fibrosis
3)Congenital lung disease
4)Esophageal atresia repair
5)Human
immunodeficiency virus(HIV)
6)Immotile cilia syndrome
7)Tuberclusis
خانم دكتر مريم مخملباف
رزيدنت بيمارستان شهدا

بسم الله الرحمن الرحیم
Problem
list:
Cough and wheeze
from neonatal
Increase in
respiratory problem from 4 m ago
Hx of atresia and
GER surgery
frequent pul
infection
FTT
CT FINDINGS :
Segmental lower
lobe collapse with cylindrical bronchectasia
Tree in bud
Neg important:
sweat test neg (1
time), smear TB neg,PPD neg, clubbing neg, immunologig? Neg
Approach to
brochectasia with anatomic anomaly
Missing
points:
ESR, HB, Alb ?
ABG?
Growth Index (Cilliary
diskinesia)
Survey of GERD and
barium meal after surjery
Immunodeficiency
tests?
IgE , Prick tese?
(sensitivity to Aspergillus)
BALL?
Stool Exam (Fatty
stool)
Sweet test (one
time only?)
Background problem
CF
GERD
Asthma
Cilliary diskinesia
TEF
(Other
anatomiCdefects such as: Sequestration,
broncogenic cyst ,
Pulmonary agenesis)
Immunodeficiency
Acquired bronchial
obstruction:(Middle lobe syndrome, CGD, granulomatose)
alpha-1 antitrypsin
9.
CF
Respiratory
complications:
Recurrent
bronchitis and pneumonia
Atelectasis
Bronchiectasis
Gastrointestinal
complications:
Esophageal atresi
CT: Segmental
lower lobe collapse with cylindrical bronchectasia
Tree in bud
Dx:
1)Sweat test
False-negative :hypoproteinemic
edema
2) Mutation
analysis
3)72-hour fecal fat
measurement
GERD:
Complications:
failure to thrive, or chronic/recurrent respiratory tract disease and anemia.
CT:
Segmental lower
lobe collapse
cylindrical
bronchectasia
Tree in bud
Complications of
fundoplication include paraesophageal hernia, and wrap failure with recurrent
GER
GERD contributes
significantly to the respiratory disease (reactive airway disease) that often
complicates EA and TEF and also worsens the frequent anastomotic strictures
after repair of EA.
ASTHMA:
بهبود مختصر با برونکودیلاتورها:
افزایش حساسیت راه های هوایی
Cilliary diskinesia:
CT: Segmental
lower lobe collapse
cylindrical
bronchectasia
Tree in bud
TEF:Complications
of surgery include anastomotic leak, re-fistulization, and anastomotic
stricture.
Immunodeficiency:
CGD, Combined
( only resiratory
problems, No diarrhea, No mouth Trust, No abNL reaction to vaccina)
Acquired bronchial
obstruction
Acute
problems:
1.BOOP
2.ABAPA
3.TB
4.Infections:
pertusis , measles
5. bronchiolitis
obliterans
Idiopathic 25%
chronic bac bronchitis
BOOP:
adenovirus,
Mycoplasma, measles, legionella, influenza, pertussis, TB
CT:
Segmental lower
lobe collapse
bronchectasia
Tree in bud
and mosaic pattern
In intact lung or
lung withbackground problems
ABAPA:
CF and Asthma
CT: Segmental
lower lobe collapse
cylindrical
bronchectasia
Tree in bud
TB
Congenital
tuberculosis is rare because the most common result of female genital tract
tuberculosis is infertility.
PPD :negative, BK :
negative
GASTRIC WASHING?
خانم دكتر سولماز حسني
رزيدنت بيمارستان امام حسين

بسمه تعالی
هوالشافی
Radiologic Finding
CXR : straggly ,
Bilateral , Infiltration ,grand glass
CT: -segmental
collapse -Tree in
bud
-Cylindrical bronchietasis -Dilation of esophagus and hiatal hernia
Bronchoscopy :
NL Mass: negative Stenosis: negative PPD: negative
Sputum: negative Allergy: negative
DH: Anti reflux ,
Anti Biotic , Bronchodilator
Wt=14.80 kg
B.WT=2.350kg HC=33.5 cm
Problem list
A 6 years old
girls presented with fever
Cough from birth
day
Weight : loss
Confined cycle of
infection
Reflux
è
operation in 1.5 years ago
CF :negative
Immunodeficiency
state: negative
EA=operation
Spo2: low(in
birth day)
Ph/E
Chest:
- inter costal
refraction -Expiration phase in long more than inspiration phase
Lung
auscultation:
- Generalized
expiratory wheezing & bilateral crackles
Lab
Data
Wbc =24300 Neut=90%
lymph=10%
RBC = 5.6
MCV= 50
PH = 605000
Bun=7
Cr=0.7
DD
Complication of surgery :
Anastomotic
leak -refistulization
-Anastomotic
stricture
GERD complicates
Non-CF related Bronchictasis
.Bronchopulmonary
sequestration (intralobar)
.Congenital
anatomic defects:
-Williams-
Campbell syndrome
-Mounier kuhn
syndrome
.Acquired
bronchial obstruction:
-middle lobe
syndrome
Foreign body
aspiration
.Abnormal
secretion clearance
.Neuromuscular
Weakness
.Primary ciliary
dyskenesia (PCD)
Non-CF related Bronchictasis
Immunodeficiency
:
-HIV
-Agammaglobulinemia
-SCID
-Digeorge
syndrome
-CGD
Non-CF related
Bronchictasis
Infection:
-Persistent
bacterial bronchitis
-Pertussis and
measles
-Mycoplasma
pneumonia
-Adenovirus
infections
-Mycobactrial
infection
.Other disorder:
-Allergic
bronchopulmonary aspergillosis
-Chronic
aspiration of gastric contents
Chronic
aspiration
Videofluoroscopy
Esophageal PH
Monitoring
Nuclear
scintigraphy
Imaging and
bronchoscopy
Neurologic
dysfunction
Missed point
Bal ?
Immunologic test
?

اهداي
جوايز كتاب رباعيات حكيم عمر خيام به 4 رزيدنت
اقاي دكتر صدر
فلوشيپ ريه
اقاي دكتر مصلحي
فلوشيپ ريه

اقاي دكتر غفاري پور
فلوشيپ ريه

اقاي دكتر جفرودي
عضو هيئت علمي بيمارستان شهدا
خانم دكتر منصوري
فوق تخصص ايمونولوژي
عضو هيئت علمي بيمارستان مفيد


















