|
پروفسور محمد
حسین سلطان زاده
استاد دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
متخصص کودکان ونوزادان
طی دوره بالینی عفونی از میوکلینیک آمریکا
دبیر برگزاری کنفرانس های ماهیانه گروه اطفال
دانشگاه علوم پزشکی شهید بهشتی
|
معرفی : دکتر مهشید مهدی زاده
فوق تخصص خون اطفال
به اتفاق اعضای هیئت علمی گروه کودکان
بیمارستان لقمان حکیم
|
تشخیص
Hepatomegaly
Increased number of cells
Inflamation
Viral
Bacterial
Toxic
Storage disease
Fat (obesity,Reye
syn,malnutrition,CF,DM,TPN,..)
Glycogen
Lipid storage (Neiman
Pick,Guuaucher,Wolman)
Micellaneous(wilson ,Alpha 1 anti
tripsin def,
Hepatomegaly
Increased number of cells
Infiltration
Primary tumors
Hepatoblastoma
HCC
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Angiosarcoma
Other sarcoma
Angiolipoma
Hamartoma
Adenoma
Teratoma
Biliary cyst
Angiomyolipoma
Hemangioma
Focal nodular hyperplasia
Hepatomegaly
Secondary tumors
Lymphoma
Leukemia
Histiocytosis
Neuroblastoma
Wilms tumor
Hepatomegaly:
Increased size of vascular space
Intra hepatic obstruction (VOD,
hepatic vein thrombosis ,web)
Supra hepatic (CHF ,pericardial
diseases
Increased size of billiary space
Congenital biliary fibrosis
Caroli disease
Idiopathic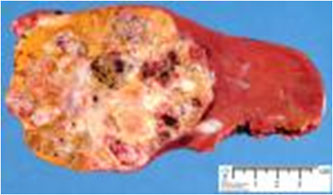
Hepatoblastoma
Mahshid Mehdizadeh MD
Pediatric Hematologist and Oncologist
Shahid Beheshti Medical University
Hepatoblastoma:
1-2% of childhood cancers
1.5/1000000 children<15 years old
2/3 of livers tumor
80% of cases reported before 3 years
of age
Median age 12-16 months
Male/Female 1.4- 2.0/1.0
The incidence is higher in far east
countries
an association between hepatoblastoma
& prematurely is suggested
-Von Gierke disease
-Congenital cystathionuria and
hemihypertrophy
-Beckwith-Wiedmann syndrom
-Trisomy 18
-Gardner syndrome
-Glycogen storage disease type 1
-Prader –Willi syndrome
-Familial adenomatosis poloposis
-Metal & petroleum exposure
-Hormone therapy (OCP)
Hepatocellular carcinoma
-Cirrhosis
-Chronic carrier of hepatitis B
-Tyrosinemia
-Glycogen storage disease type 1
-Neurofibromatosis
-Alagille syndrom
-Alpha 1anti tripsin deficiency
=Wilms tumor teated with radiation
-Methotraxate
-Fanconi anemia
-Ataxia-telangiectasia
Geographic Distribution of HBV Carriers and Incidence of Hepatoma
Hepatoblastoma:
-Von Gierke disease
-Hemi hypertrophy
-Beckwith-Wiedmann syndrom
-Umbilical hernia
-Congenital absence of kidney
-Congenital absence of adrenal
-Meckels diverticulum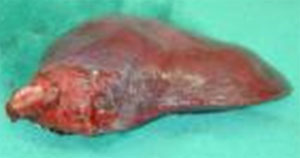
Epithelial type
Embryonal pattern
Fetal pattern
Macrotrabecular type
Small-cell undifferentiated type or
anaplastic
Mixed epithelial and mesenchymal type
Hepatoblastoma:Clinical manifestations:
Abdominal mass 80%
Abdominal distention 27%
Anorexia
20%
Weight loss
19%
Abdominal pain 15%
Pallor 7%
Jaundice (rare) 5%
Fever 4%
Diarrhea
2%
Costipation
Precocious puberty in male(occ)
1%
The clinical manifestations of
hepatoblastoma and hapatocelluar carcinoma are similar
Hepatoblastoma: Diagnostic evaluation: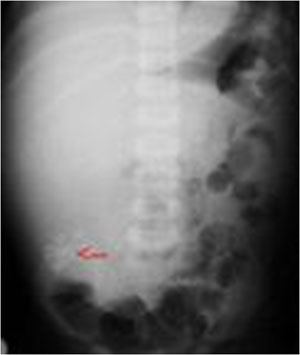
-Extent of intrahepatic disease
Sonogrsphy
CT scan
MRI imaging
-Potential for hepatic resectability
-Presence or absence of extrahepatic
disease
Lung
Bone
Bone marrow(very rarely)
CBC
Anemia
Thrombocytosis
Liver enzyme (usually normal or mildly
elevated
Hepatitis B
AFP
Beta HCG
CEA
Hepatoblastoma:
AFP
is elevated in 90% of patients with
hepatoblastoma and 50% of patient with HCC ( normal<10 ng/ml)
is a marker of monitoring residual and
metastatic disease
serial measurement should be done
Hepatoblastoma:Staging:
POG/CCG staging
1:completely resectable
2:Microscopic residual disease
3:Gross residual disease
4: Distant metastasis
International society of pediatric
oncology staging
PRETEXT
Hepatoblastoma :treatment: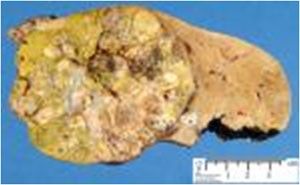
Surgury
Chemotherapy(5FU,vincristine,
doxorubicin,cisplatin)
Radiation ?
Liver transplantation
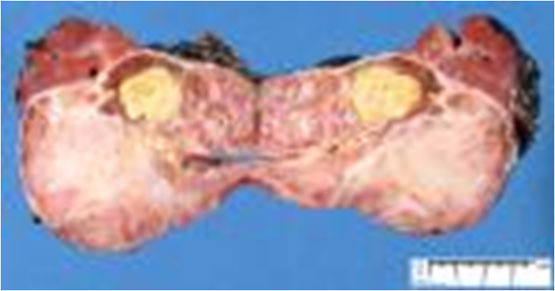
Hepatoblastoma: prognosis :
Surgury and complete tumor resection
Degree of mitotic activity (pathology,
flow cytometry)
Fetal histology(good)
Reduction of alpha feto protein by
chemotherapy (unresectable tumors)
Diploid tumors are better