|
|
تشخیص:
WEGENER,S
GRANULOMATOSIS
خانم دکتر جدلی پاتولوژیست
خانم دکتر هاشمی رزیدنت بیمارستان کودکان مفید
خانم دکتر مهسا مهری
رزیدنت بیمازستان امام حسین
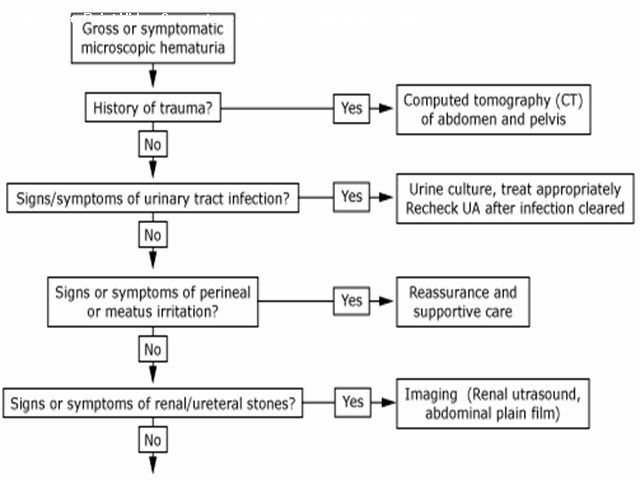
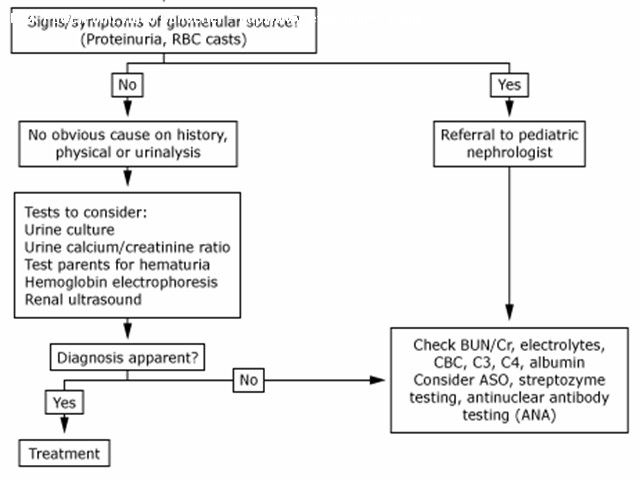
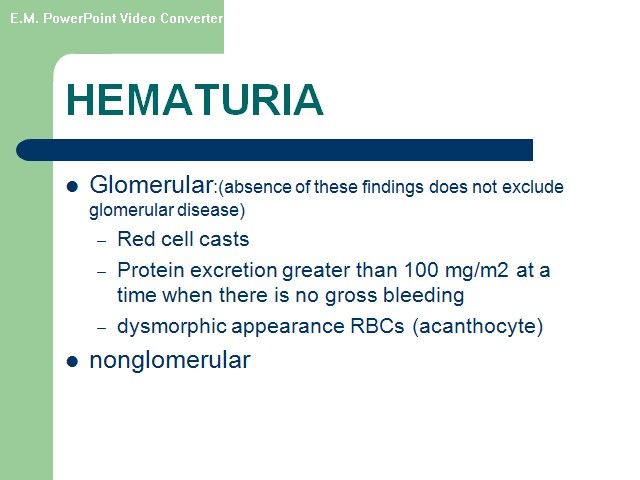
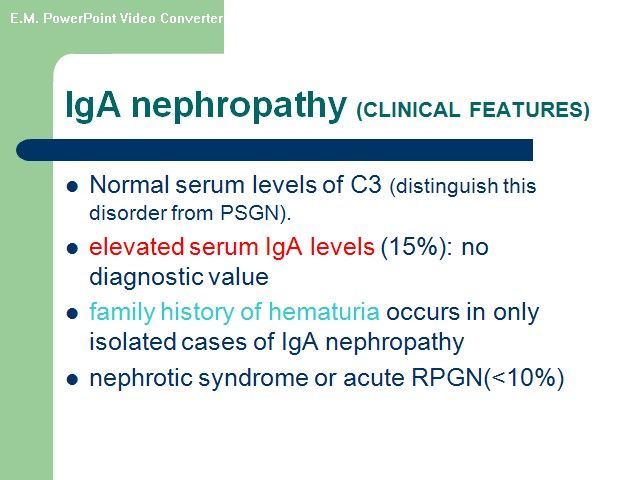
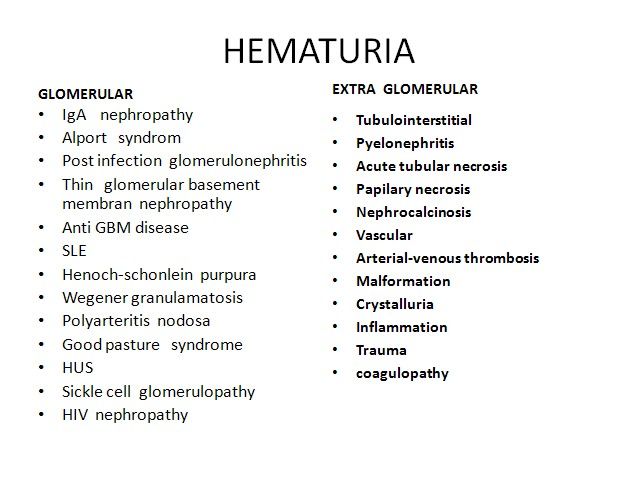
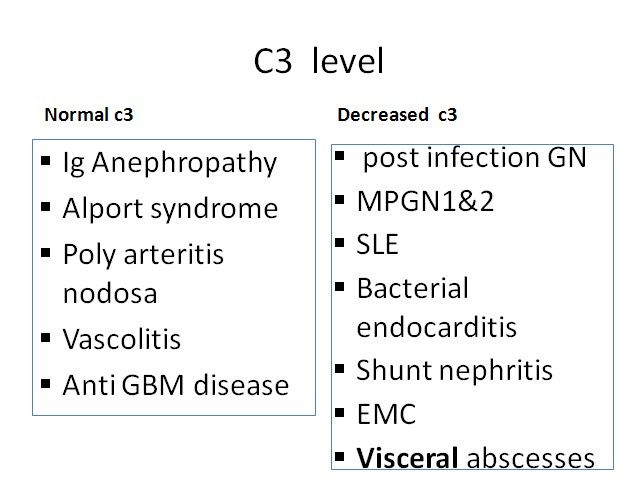
اقای دکتر هوشیار رزیدنت بیمارستان لقمان Hematuria Glomerular arly-morning periorbital puffiness •weight gain •oliguria, • the presence of dark-colored urine, and edema or hypertension •painless •joint pains •skin rashes prolonged fever Non glomerural •history of passage of clots in urine •fever • abdominal pain • dysuria, frequency, and enuresis •recent trauma to the abdomen GLOMERULAR HEMATURIA Isolated Renal Disease •IgA nephropathy (Berger disease) •Alport syndrome (hereditary nephritis) •Thin glomerular basement membrane nephropathy •Postinfectious GN (poststreptococcal GN) •Membranous nephropathy • Membranoproliferative GN • Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis • Antiglomerular basement membrane disease GLOMERULAR HEMATURIA Multisystem Disease •Systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis • Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis • Wegener granulomatosis •Polyarteritis nodosa •Goodpasture syndrome •Hemolytic-uremic syndrome •Sickle cell glomerulopathy • HIV nephropathy Hematuria with familial association
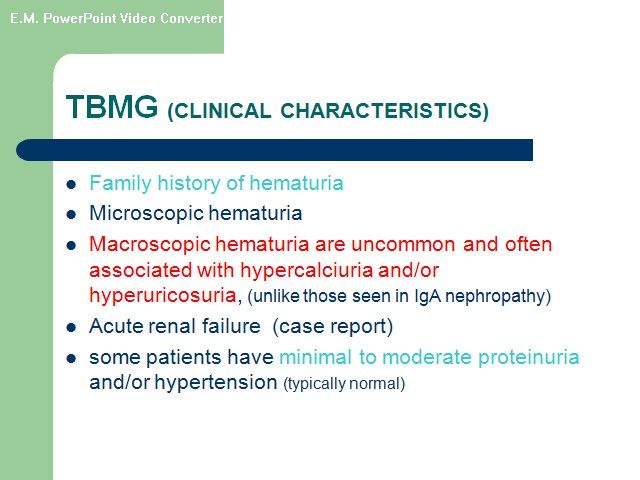
- Benign Familial Hematuria ( Thin Membrane Disease )
- Alport syndrome
- Idiopathic Hypercalciuria
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Urolithiasis
- Tumors
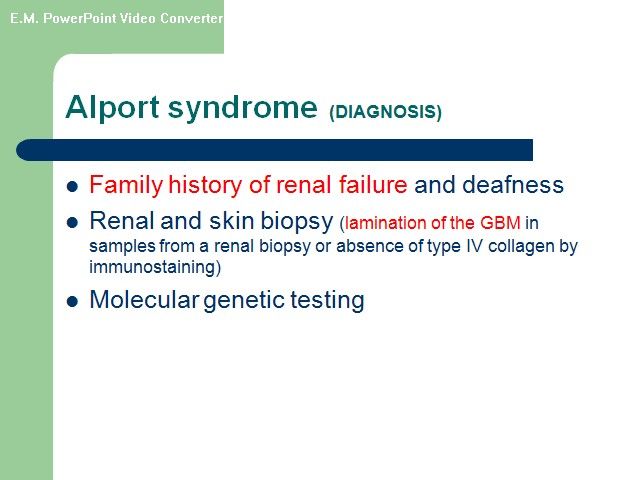
Alport Syndrome Its classically X-linked form, suggested by hematuria in a male. Positive family history of hematuria, deafness, and renal failure. Abnormal collagen IV composition.
Alport syndrome - hereditary disorder of GBM
Hearing defects
Diagnosis of Alport syndrome
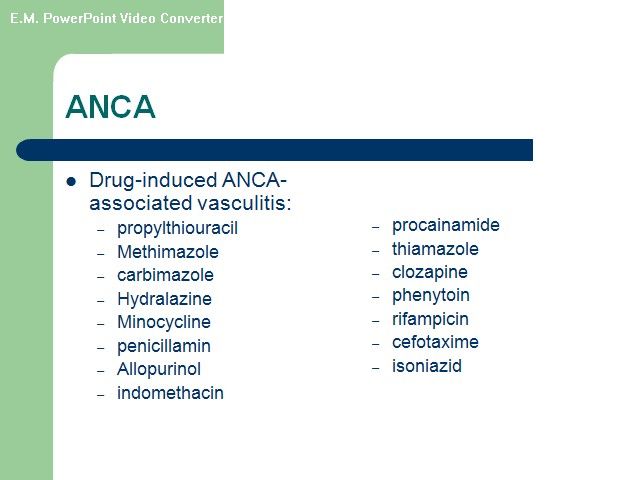
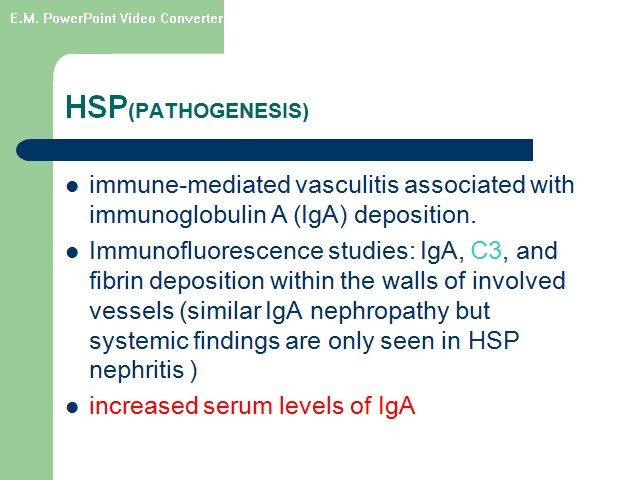
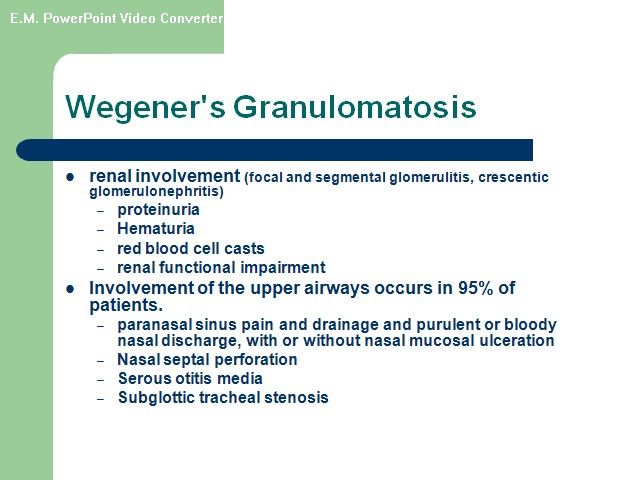
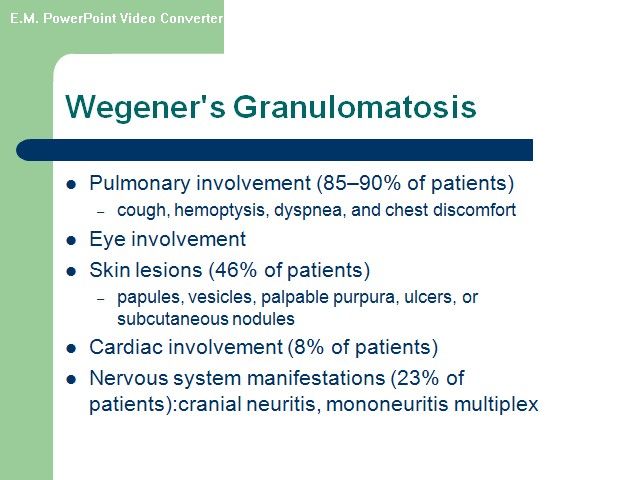
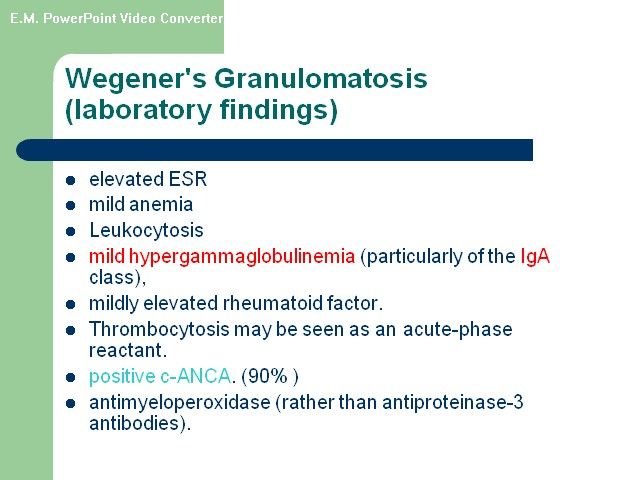
ANCA-associated” Disorders •Wegener granulomatosis • Microscopic polyangiitis • Churg-Strauss syndrome Wegener's granulomatosis (WG) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) •WG and MPA are related systemic vasculitides •Both are associated with (ANCA) and have similar features on renal histology(a focal necrotizing, pauci-immuneglomerulonephritis that is characterized by necrotizing glomerulonephritis with little or no deposition of immunoreactants (IgG, IgM, IgA, and complement components). •Approximately 90 to 95 percent of patients with active, generalized WG are ANCA-positive
•WG patients with ANCA, 80 to 90 percent, have PR3-ANCA(C-ANCA),and the remaining patients have MPO-ANCA(P-ANCA) •Dual positivity for both PR3- and MPO-ANCA may rarely •Approximately 70 percent of patients with MPA are ANCA-positive. In contrast to WG, most ANCA-positive MPA patients have P-ANCA, with a minority having C-ANCA.
|