|
Apporved by the advisory committee on Immunization Practices (
ACIP ) , the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) , and the American Academy of
Family Physicians (AAFP)
On October 22,1999,the Advisory committee on
Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommended that Rotashield (RRV-TV) , the only
US-licensed rotavirus , no longer be used in the United States (MMWR Morb Mortal
Wkly Rep.Nov 5 , 1999 ; 48(43):1007).Parents should be reassured that their
children who received rotavirus vaccine before july are not at increased risk
for .intussusception now
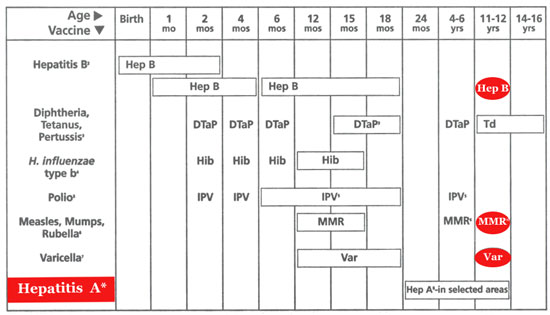
1.This schedule indicates the
recommended ages for routine administration of currently licensed childhood
vaccines as of 11/1/99 . Additional vaccines may be licensed and recommended
during the year .Licensed combination vaccines may be used whenever any
components of the combination are indicated and its other components are not
contraindicated . Providers should consult the manufacturers’ package
inserts for detailed recommendations.
2. Infants born to HBsAg-negative
mothers should receive the1st dose of hepatitits B (Hep B) vaccine by
age 2 months . The 2 nd dose should be at least 1 month after the 1
st dose. The 3 rd dose should be administered at least 4 months after the 1st
dose and at least 2 mothers after the 2 nd dose , but not before 6 months of age
for infants .
Infants born to HBsAg-positive
mothers should receive hepatitis B vaccine and 0.5 ml hepatitis B immune
globulin (HBIG ) within 12 hours of birth at separate sites . The 2 nd dose is
recommended at 1 to 2 months of age and the 3 rd dose at 6 months of age.
Infants born to mothers whose HBsAg
status is unknown should receive hepatitis B vaccine whithin 12 hours of
birth . Maternal blood should be drawn at the time of delivery to detemine the
mother’s HBsAg status; if the HbsAg test is positive,the infant should receive
HBIG as soon as possible (no later than 1 week of age).
All children and adolescents (through
18 year of age) who have not been immunized against hepatitis B may
begin the series during any visit.special efforts should be made to immunize
children who were born in or whose parents were born in areas of the world with
moderate or high endemicity of hapatitis B virus infection.
3.
The 4 th dose of DTaP (diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and
acellular pertussis vaccine ) may be administered as early as 12 months of
age , provided 6 months have elapsed since the 3 rd dose and the child is
unlikely to return at age 15 to 18 months .Td (tetanus and diphtheria toxoids )
is recommended at 11 to 12 years of age if at least 5 years have elapsed since
the last dose of DTP,DTaP or DT. Subsequent routine Td boosters are recommended
every 10 years.
4.
Three Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) conjugate vaccines are
licensed for infant use . If PRP-OMP ( PedavaxHIB or ComVax [Merck]) is
administered at 2 and 4 months of age ,a dose at 6 months is not required
.Because clinical studies in infants have demonstrated that using some
combination products may induce a lower immune response to the Hib vaccine
component , DtaP/Hib combnation products should not be used for primay
immunization in infants at 2,4,or 6 months of age unless FDA-approved for these
ages.
5.
To eliminate the risk of vaccine –associated paralvtic polio (VAPP)
.an all-IPV schedule is now recommended for routine childhood polio vaccination
in the United States .all children should receive four doses of IPV at 2 months
, 4 months , 6 to 18 months , and 4 to 6 vears .OPV (if available)may be used
only for the following special circumstances:
1. Mass vaccination
campaigns to control outbreaks of paralytic polio.
2. Unvaccinated
children who will be traveling in <4 weeks to areas where polio is endemic or
epidemic.
3. Children of
parents who do not accept the recommended number of vaccine injections.These
children may receive OPV only for the third or fourth dose or both; in this
situation health care professionals should administer OPV only after discussing
the risk for VAPP with parents or caregivers.
4. During the transition
to an all-IPV schedule ,recommendations for the use of remaining OPV supplies in
physicians’ offices and clinics have been issued by the American Academy of
pediatrics (see Pediatrics ,December 1999).
6.The 2 nd dose of measles , mumps ,
and rubella (MMR) vaccine is recommended routinely at 4 to 6 years of age but
may be administered during any visit , provided at least 4 weeks have elapsed
since receipt of the 1 st dose and that both doses are administered beginning at
or after 12 months of age . those who have not previously received the second
dose should complete the schedule by the 11-to 12-year-old visit.
7.Varicella (Var) vaccine is
recommended at any visit on or after the first birthday for susceptible children
, ie , those who lack a reliable history of chickenpox (as judged by a health
care professional ) and who have not been immunized.Susceptible persons 13 years
of age or older should receive 2 doses , given at least 4 weeks apart .
8. Heapatitis A(Hep A) is
shaded to indicate its recommended use in selected stats and/or regions;consult
your local public health authority.(Also see MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.Oct 01,
1999;48 (RR-12):1-37).
Recomended
Immunization Schedules for
Children Not Immunized in the First Year
of Life*
* Table is not
completely consistent with package inserts.For products used,also consult
manufacturers package insert for instructions on storage , handling,dosage,and
administration.Biologics prepared by different manufacturers may very , and
package insers of the same manufacturer may change.Therefore , the physician
should be aware of the contents of the current package insert.Vaccine
abbreviations: HBV indicates hepatitis B virus; Var ,varicella;DtaP , diphtheria
and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis;Hib Haemophilus influenzae type b
Conjugate;IPV , inactivated poliovirus;MMR,live measles – mumps – rubella: dT,
adult tetanus toxoid (full dose)and diphtheria toxoid (reduced dose ),for
children 7 years of age or older and adults.
If all needed vaccines cannot be
administered simultaneously,priority should be given to protecting the child
against the diseases that pose the greatest immediate risk.
In the United States , these diseases for
children younger than 2 years usually are measles and Haemophilus influenzae
type b infection;for children older than 7 years,they are measles,mumps , and
rubella.Before 13 years of age , immunity against hepatitis B and vericella
should be ensured.DtaP , HBV,Hib , MMR,and Var can be given simultaneously at
separate sites if faliure of the patient to return for future immunizations is a
concern.For further information on pertussis and poliomyelitis immunization .icella
vaccine can be administered to susceptible children any time after 12 months of
age.Unimmunized children who lack a reliable history of Varicella should be
immunization before their 13 th birthday.
Minimal interval between doses of MMR is 1
month(4wk).
HBV may be given earlier in a 0-,2-,and
4-month schedule. | 


